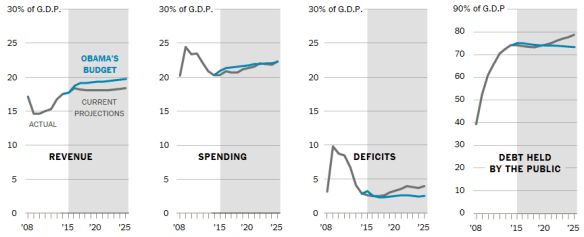
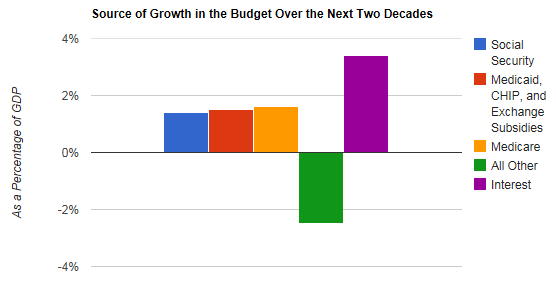Tax Day is a good time to remind ourselves about our perilous fiscal situation. With a public debt (on which we pay interest) of $13 trillion and with annual deficits of just under $500 billion adding to the debt each year, we have a huge problem which is not being adequately addressed by Congress. The solution is to either raise taxes or cut spending or do a combination of both.
 Is it feasible to raise taxes, presumably on the rich? The problem in doing this is that our tax code is already very progressive as indicated by the above chart. The top 20% already pay 84% of all income taxes. It’s just not feasible to expect to be able to raise their taxes by a very large amount. In addition, Middle- and lower-income people are in a tight fiscal situation, because of the slow economy, and can hardly be expected to see their own taxes increase.
Is it feasible to raise taxes, presumably on the rich? The problem in doing this is that our tax code is already very progressive as indicated by the above chart. The top 20% already pay 84% of all income taxes. It’s just not feasible to expect to be able to raise their taxes by a very large amount. In addition, Middle- and lower-income people are in a tight fiscal situation, because of the slow economy, and can hardly be expected to see their own taxes increase.
 The alternative to raising taxes is to cut spending and there are many opportunities to do this. The organization Citizens Against Government Waste has just identified a collection of government programs whose elimination would save $639 billion in the first year alone. Taxpayers for Common Sense has a long list of potential spending cuts which would save $267 billion in the first year.
The alternative to raising taxes is to cut spending and there are many opportunities to do this. The organization Citizens Against Government Waste has just identified a collection of government programs whose elimination would save $639 billion in the first year alone. Taxpayers for Common Sense has a long list of potential spending cuts which would save $267 billion in the first year.
Amazingly, neither of these lists of possible cuts includes any mention of entitlement programs. Before very long, major savings in entitlement programs must certainly be achieved in order to put the federal government on a sustainable fiscal course.
In fact, spending should be trimmed all across the board, wherever possible, in order to get our annual deficits on a steadily downward course. It is critical for this process to get under way as soon as possible and to continue until fiscal balance is achieved by entirely eliminating deficit spending altogether.