“Life’s tragedy is that we get old too soon and wise too late”
Benjamin Franklin, 1706 – 1790
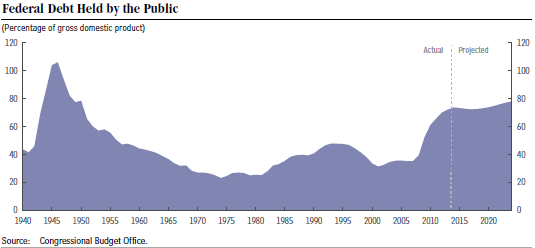 The above chart from the Congressional Budget Office’s latest budget forecast “Updated Budget Projections: 2014 to 2024” shows very clearly how the public debt (on which we pay interest) has climbed dramatically in the last six years, as a percentage of GDP, and is projected to keep on growing indefinitely. As the economy improves and interest rates return to normal levels, interest payments on the debt will skyrocket and become a permanent drag on future growth.
The above chart from the Congressional Budget Office’s latest budget forecast “Updated Budget Projections: 2014 to 2024” shows very clearly how the public debt (on which we pay interest) has climbed dramatically in the last six years, as a percentage of GDP, and is projected to keep on growing indefinitely. As the economy improves and interest rates return to normal levels, interest payments on the debt will skyrocket and become a permanent drag on future growth.
In a recent post “How to Control Federal Spending: The Highway Trust Fund” I pointed out that thanks to the Budget Sequester Act from 2011, it is unlikely that the $35 billion Highway Trust Fund, supported by an 18.2 cent per gallon federal gasoline tax, will be supplemented by general government revenue, paid for by increasing the deficit. In other words, discretionary spending is under control at the present time due to the ten year sequester limits.
But this makes up less than 1/3 of the federal budget, the rest being “mandatory” entitlement spending, for such programs as Social Security, Medicare and Medicaid. This is where the huge projected future growth in overall federal spending comes from and therefore where we need to focus on budget control. The huge challenge is that the number of Americans who are retired, now about 50 million, is growing rapidly. Furthermore, older citizens vote in greater proportion than any other age group and don’t want their benefits to be cut. Elected representatives need help to resist the pressure from senior citizens for greater benefits. Here are two possible ways to provide this help:
- A Balanced Budget Amendment to the U.S. Constitution. It would have to be flexible enough to allow overrides for emergencies by a supermajority vote, but otherwise it would force Congress to either cut spending or else raise taxes to bring in more revenue. The tradeoff between these two alternatives would create the discipline to make the hard choices required.
- Term Limits for national office. I would choose 12 year limits for both the Senate and the House of Representatives but other choices are possible. Knowing that one’s time in office is limited will help provide the strength to make the difficult decisions to either cut spending or raise tax revenue. New members of Congress are more independent thinking than the careerists whose main goal is to get reelected.
Either of these two possible changes in the rules would help turn things around. We need to do something before we have another financial crisis much worse than the last one!

