Not only is Washington politics already hyper-partisan, but both parties are continuing to move to even greater extremes, see here and here.
Here are two examples of extreme positions now being espoused by major elements of one or the other of the two parties:
- Single payer healthcare. The failure of the GOP effort to repeal the Affordable Care Act this past summer means that (the goal of) universal healthcare is here to stay. The ACA expands access to healthcare but does nothing to control costs. Single payer, Medicare for All, would control costs but then we end up with socialized medicine. The only way to establish a cost efficient free market healthcare system is to remove, or at least limit, the tax exemption for employer provided care and to set up high deductible catastrophic care supplemented by health savings accounts to pay for routine expenses. This would compel everyone to pay close attention to the cost of their own healthcare.

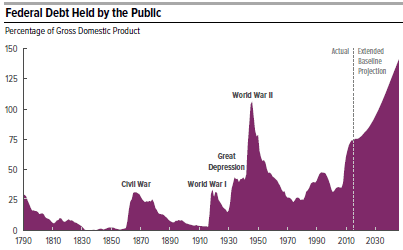
- Tax cuts instead of tax reform. Tax reform, i.e. lowering both corporate and individual tax rates, paid for by closing loopholes and shrinking deductions, is an excellent way to speed up economic growth and thereby create more and better paying jobs. But it is imperative to do this in a revenue neutral manner, i.e. without increasing our annual deficits. Our debt (the public part on which we pay interest) now stands at 77% of GDP, the highest it has been since the end of WWII, and is predicted by the Congressional Budget Office to keep getting larger without major changes in public policy.
Conclusion. The U.S. badly needs a more cost efficient healthcare system and a simpler and more efficient tax system. But there are right ways and wrong ways to do both of these things. Single payer healthcare and (unpaid for) tax rate cuts are the wrong way to proceed. In each case, no action at all is much better than getting it wrong.