My last two blogs were “Why racism exists in America” and “Educare and the Academic Achievement Gap.” I often describe myself as a fiscal conservative but it would be more accurate to say that I am a fiscal conservative with a social conscience.
 By this I mean:
By this I mean:
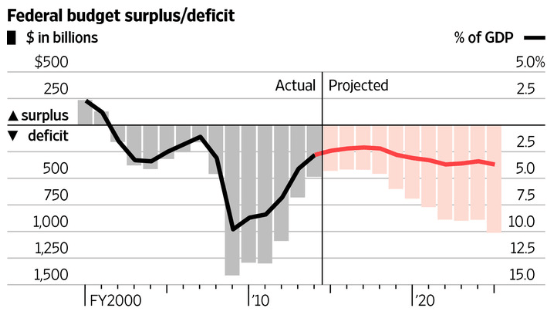
- First and foremost I want to shrink our annual federal budget deficits enough so that our national debt begins to decline as a percentage of GDP. Right now the public debt (on which we pay interest) is at 74% of GDP which is the highest it has been since the end of WWII. This high level of debt is unsustainable and will inevitably lead to a new and much worse financial crisis if it is not put on a downward path.
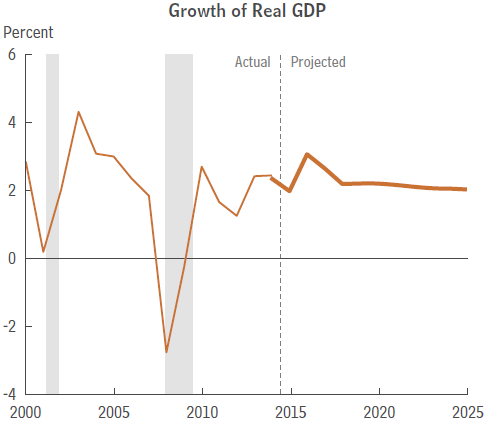
- Closely related to the first goal is the need to get our economy growing faster than the 2% average rate of growth since the end of the Great Recession in June 2009. This will have the twin benefits of producing more tax revenue which will make it easier to shrink our annual budget deficits as well as creating more and better paying jobs for everyone.
- A third goal is to reduce income inequality. The best way to do this is not with more income redistribution from those with higher incomes to those with lower incomes but rather by achieving faster economic growth which will raise incomes for all. Yet another critical way of making American society more equal is to focus on:
- Reducing social inequality. There are many different forms of social inequality in our society but let’s focus on one of the most severe aspects: black-white racism. America will be a more peaceful and prosperous country if we can reduce the glaring inequalities between the two races.
I am sufficiently optimistic to think it is possible to make progress on all of these fronts at the same time. It won’t be easy but momentum is slowly but surely building in this direction.