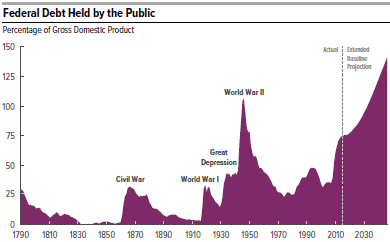
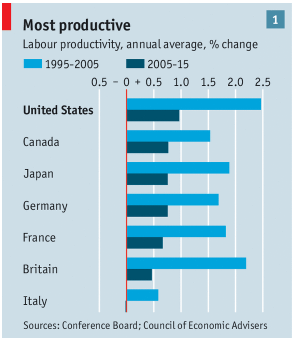
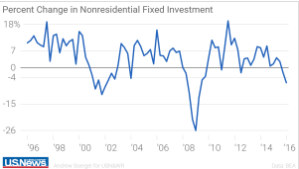
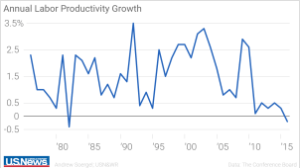
President-elect Donald Trump has nominated a charter school advocate from Michigan, Betsy DeVos, to be his Secretary of Education. This raises the obvious question, do charter schools improve K-12 education? A recent study by Stanford University’s Center for Research on Education Outcomes (CREDO) suggests that they do in general, although very unevenly.
As summarized and elaborated upon by the Economist, here are the results:
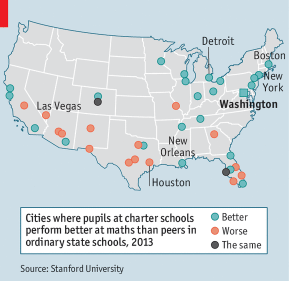
- Charter schools work well for low-income children in cities. In 41 urban areas (see map), students learned 40 more days of math and 28 more days of reading every year on average. Black and Hispanic children performed especially well. Where they have worked well such as in Boston, New York City and Washington D.C., students make gains up to 100 days per year.
- One lesson learned is that autonomy needs to be coupled with accountability. When charter schools expand with little oversight, as in Arizona, results can be worse than in regular schools.
- A second lesson is that leadership matters. Business practices such as performance tracking and incentives achieve better test scores. A successful charter organization such as KIPP (Knowledge is Power Program) opens new school only when it spots a leader capable of running it.
- A third lesson is how to scale up the type of education provided by the best charters. These have five qualities: frequent feedback for teachers, tutoring, longer school days and terms, effective use of data to track student progress, and a relentless focus on academic achievement.
Conclusion. Charter schools are a valuable state and local educational option. Many charters are succeeding very well and the factors which lead to success are increasingly well understood. At the very least the competition created by charter schools leads to better performance by public schools. The answer to the question in the title is yes!