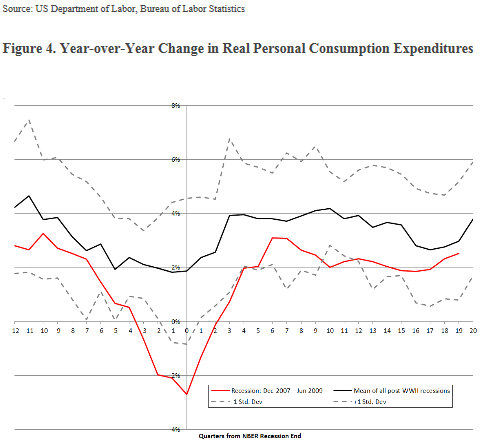
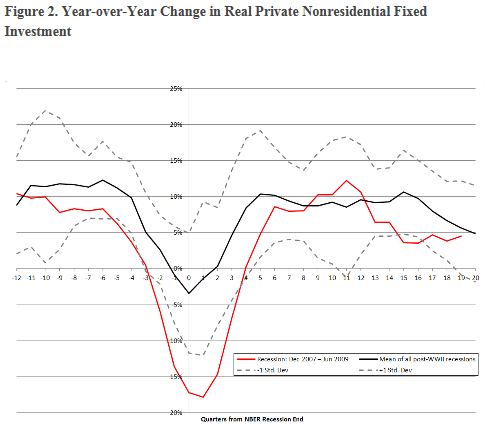
The financial crisis of 2008 was the biggest shock to our financial system since the Great Depression of the 1930s. It caused a deep recession from which we are still recovering. To aid the recovery the Federal Reserve launched an unprecedented expansion of the money supply, referred to as quantitative easing, as well as keeping short term interest rates near zero. As explained by James Rickards, a portfolio manager at West Shore Group, in his new book, “The Death of Money, the coming collapse of the international monetary system,” such a severe recession would normally have caused a corrective period of deflation. Quantitative easing has warded off deflation and, so far, without igniting inflation.
 We are now in a catch-22 situation. Congress could and should adopt several policy changes to speed up the recovery as I described several days ago in “The Federal Reserve Cannot Revive the Economy by Itself.” But, if and when the economy does start growing faster, it will require great skill by the Fed to exit from its current policies without harm. If it contracts the money supply too quickly, it risks a sharp rise in interest rates. If it contracts the money supply too slowly, it risks a sharp rise in inflation. Mr. Rickards doubts that the Fed will be able to accomplish this fine tuning without another major crisis. Here are his Seven Signs of what to look for:
We are now in a catch-22 situation. Congress could and should adopt several policy changes to speed up the recovery as I described several days ago in “The Federal Reserve Cannot Revive the Economy by Itself.” But, if and when the economy does start growing faster, it will require great skill by the Fed to exit from its current policies without harm. If it contracts the money supply too quickly, it risks a sharp rise in interest rates. If it contracts the money supply too slowly, it risks a sharp rise in inflation. Mr. Rickards doubts that the Fed will be able to accomplish this fine tuning without another major crisis. Here are his Seven Signs of what to look for:
- The price of gold ($1300 per ounce today). A rapid rise to $2500 will anticipate inflation. A rapid decrease to $800 signals severe deflation.
- Gold’s continued acquisition by Central Banks. Large purchases by China, for example, will announce inflation.
- IMF governance reforms, e.g. towards more voting power for China, will be an inflation warning.
- The failure of regulatory reform, i.e. reinstatement of Glass-Steagall in addition to the Volcker Rule, will increase the chances of systemic failure.
- System crashes, resulting from high-speed, highly automated, high volume trading. An increasing tempo of such events will cause disequilibrium which could close markets.
- The end of QE, could give deflation a second wind and lead to a new round of QE.
- A Chinese collapse (predicted by Rickards), will lead first to deflation and then inflation.
We all hope that the Federal Reserve can steer clear of a new, and much deeper, financial crisis. But it doesn’t hurt to have guideposts and Mr. Rickards knows what he’s talking about.