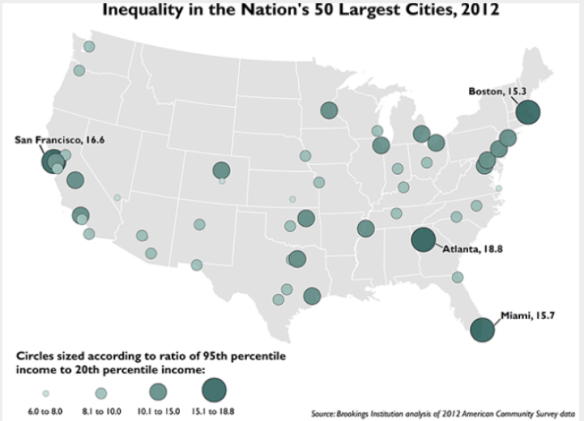
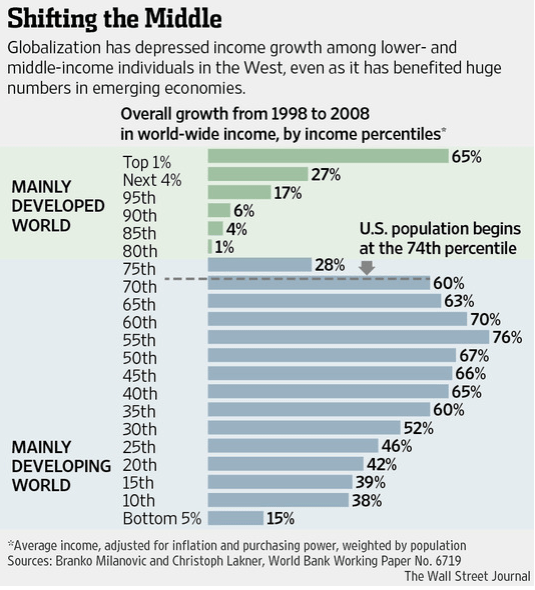
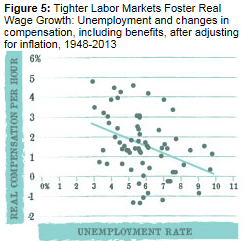
The economist Lawrence Lindsey has an Op Ed in yesterday’s Wall Street Journal analyzing Census Bureau data here, and here showing that income inequality rose more under Bill Clinton than under Ronald Reagan. It also has risen much more under Barack Obama than under George W. Bush.
 Here is the explanation for this:
Here is the explanation for this:
- Cheap money is a boon to those who have access to it.
- Bill Clinton, George W. Bush and Barack Obama all presided over bubble economies fueled by easy monetary policy. But the effects of the Bush housing bubble were more evenly distributed than for the Clinton stock market bubble or the Obama credit bubble.
- In 1968 government transfer payments totaled $53 billion or roughly 7% of personal income. By 2014, these had climbed to $2.5 trillion or 17% of personal income. Despite the redistribution of a sixth of all income, inequality is far higher today than in 1968.
- Two earner households have become the backbone of the American middle class.
- When families with children making between $20,000 and $50,000 attempt to have a second earner go back to work, the effective tax rate on the extra earnings, including lost government benefits, is between 50% and 80%. This “working class trap” is increasing income inequality and keeping the income of these households lower than they would otherwise be.
- During the first six years of the Obama presidency, the number of two-earner households declined, while the number of single-earner households rose by 2.6 million and the number of no-earner households rose by 5 million. In other words, two-thirds of the increase in the number of households under Obama is accounted for by households with no one working. This is the reason the middle class has shrunk and that inequality is increasing.
- A recent Brookings Institution study shows that boosting the top tax rate from 39.6% today to 50%, and redistributing the additional $95 billion in tax revenue to the bottom 20% of wage earners would reverse only 20% of the increase in income inequality under Obama.
As Mr. Lindsey concludes, “Attacking the rich and running against inequality may be a sensible political strategy. But in the end the programs to implement this strategy make the problem worse.”
Follow me on Twitter: https://twitter.com/jack_heidel
Follow me on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/jack.heidel.3