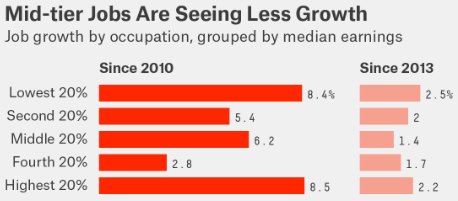
Income inequality in the U.S. is getting worse and one reason is that the middle class is being “hollowed out” by a lack of sufficient job opportunities.
 The result is more people at the bottom end of the income scale. Not surprisingly, it turns out that many of these low-wage workers are receiving public assistance, as documented by the UC Berkeley Labor Center, and the New York Times.
The result is more people at the bottom end of the income scale. Not surprisingly, it turns out that many of these low-wage workers are receiving public assistance, as documented by the UC Berkeley Labor Center, and the New York Times.
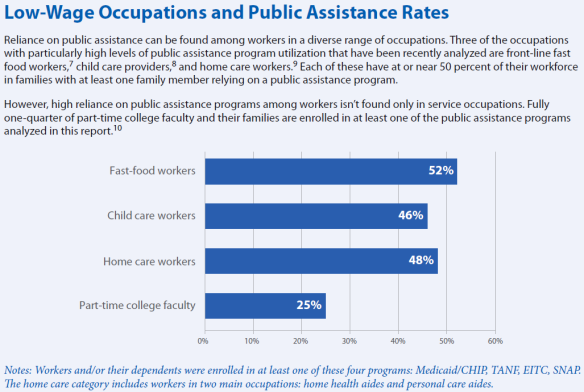 The authors point out that if these workers received higher wages, they would not require as much public support which, in turn, would save money for the taxpayers. This is a true but not a practical means for helping the poor. Employees are paid what they’re worth based on the law of supply and demand. Companies will pay as much as they have to in order to find and retain well qualified workers. Furthermore, a minimum wage which is too high will simply lead to a higher rate of unemployment.
The authors point out that if these workers received higher wages, they would not require as much public support which, in turn, would save money for the taxpayers. This is a true but not a practical means for helping the poor. Employees are paid what they’re worth based on the law of supply and demand. Companies will pay as much as they have to in order to find and retain well qualified workers. Furthermore, a minimum wage which is too high will simply lead to a higher rate of unemployment.
There is really only one good way to raise the overall wage level, especially at the bottom end of the scale. It is to speed up economic growth, thereby lowering the unemployment rate and creating more demand for workers.
This is exactly what has happened in Omaha NE where I live. The official unemployment rate is 3.2% and there is a labor shortage. A new minimum wage ($8/hour now, $9/hour next January) was approved by the voters last November. But low-skill entry level jobs are paying $10/hour or more because of the scarcity of workers.
There are plenty of opportunities to succeed in Omaha. Support yourself with a low-wage job and go to Metropolitan Community College to learn a high-skill, high-wage trade. Most people are capable of following this route to a better life!