This website, It Does Not Add Up, is devoted to discussing our country’s most serious economic and fiscal problems. They are:
- Stagnant Economy. Since the end of the Great Recession in June 2009, the economy has been growing on average at the historically slow rate of about 2.3%. Slow growth means higher unemployment, stagnant wages and less tax revenue.
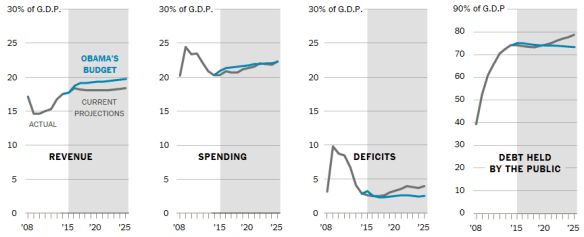
- Massive Debt. U.S. public (on which we pay interest) debt is now 74% of GDP (highest since WW II) and projected by CBO to grow rapidly unless strong measures are taken to reduce it. This puts our country’s future wellbeing and prosperity at great risk.
- Increasing Income Inequality. Incomes for the high-skilled and well-educated are increasing much faster than for the low-skilled and less-educated workers.
The new Republican majorities in Congress are stirring the waters by proposing a ten year plan to shrink the deficit down to zero, i.e. to balance the budget by 2025. The opposition claims that this would “sharply cut the scale of domestic spending, which would mostly fall on the poor.”
 But the American Enterprise Institute’s James Pethokoukis points out that social spending in the U.S., both public and private, is very generous and second only to France in the entire OECD. So here is how we could proceed to address our basic problems in a unified manner:
But the American Enterprise Institute’s James Pethokoukis points out that social spending in the U.S., both public and private, is very generous and second only to France in the entire OECD. So here is how we could proceed to address our basic problems in a unified manner:
- Balance the Budget by a combination of Republican spending cuts and cutting back on two major tax deductions: Employer-sponsored Health Insurance (cost: $250 billion per year) and Mortgage Interest (cost: $70 billion per year).
- Boost Economic Growth by expanding the Earned Income Tax Credit to encourage more people to accept low paying, entry level jobs. Increase the Social Security eligibility age from 67 to 70, thereby keeping near retirees in the workforce for three additional years (this will also extend the solvency of the Social Security Trust Fund).
- Decrease Income Inequality. Cutting back on tax deductions, in part to pay for expansion of the EITC, lessens income inequality as well as shrinking the deficit. A faster growing economy also lessens inequality by providing more opportunities for upward mobility.
In other words, addressing each of these fundamental problems in an intelligent manner contributes to solving the remaining problems as well. This creates a virtuous circle for economic progress!