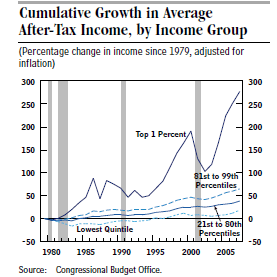
I have had many recent posts addressing the problem of income inequality in the United States and what can and should be done about it. Below is a chart, from the Congressional Budget office, which also appeared in my December 24, 2013 post. It shows that all income groups have made gains since 1980 but that higher income groups have gained the most.
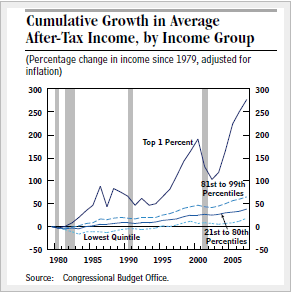 This means that income inequality is increasing. The question is what to do about it. My own attitude is to try to provide more economic opportunity for low income people. How do we do this in the most effective way?
This means that income inequality is increasing. The question is what to do about it. My own attitude is to try to provide more economic opportunity for low income people. How do we do this in the most effective way?
- First and foremost by stimulating the private economy to grow faster and therefore to create more and higher paying jobs. This can be done with broad based tax reform (lowering tax rates offset by closing loopholes), fiscal stability achieved by eliminating deficit spending, expanded foreign trade for a more efficient global economy, and finally, immigration reform to give legal status to undocumented workers and allow more high skilled foreigners to immigrate to the U.S. Such measures as these require action by Congress and the President.
- Secondly, by improving human capital, meaning fixing underperforming schools, improving rundown neighborhoods, combatting inner city crime more effectively, providing at least part-time jobs to young people and combatting teenage pregnancy. Problems such as these are best addressed at the state and local level.
- Finally, providing more motivation for the unemployed and underemployed to find jobs and hold onto them. A very effective way to do this is with the federal Earned Income Tax Credit. It supplements the salary of working adults with children. New York City is conducting an experiment to see if a similar program will also motivate childless adults to try harder to find work and stay employed.
Conclusion: the best way to address inequality is to give people the best possible opportunity to obtain full time employment. This means 1) creating more jobs, 2) providing better qualified workers for all jobs and 3) motivating the unemployed more strongly to find jobs and hold on to them.
Government at all levels can help people find jobs, in one way or another, and therefore become more productive citizens. This will lead to a happier, healthier, and therefore a stronger society. All of us will benefit from this happening!