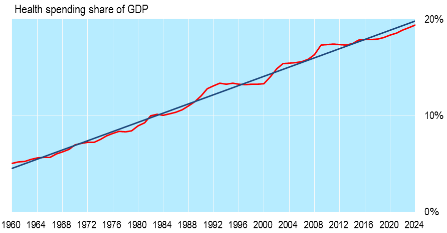
Most of the controversy generated by the healthcare bill passed by the House, and the one now being considered by the Senate, concerns the way Medicaid is funded. The current system whereby states are reimbursed by the federal government for a percentage (national average 53%) of their Medicaid expenses would be replaced by putting the federal contribution on a strict per-capita basis, indexed to the annual rate of inflation.
Medicaid is a vast program now serving 73 million low-income and disabled Americans and is doing a good job especially for the elderly and the disabled with special needs. But it costs the federal government nearly $400 billion per year and the cost is growing rapidly. It is essential to get open-ended Medicaid spending under much better control and one good way to do this is to put the federal contribution on a fixed budget.

The Congressional Budget Office has just issued its latest Budget and Economic Outlook report. It shows the ever-worsening fiscal condition for the U.S., unless current policy is changed.
- The deficit for 2017 is predicted to be $693 billion or 3.6% of GDP.
- Deficits will grow dramatically over the next decade with trillion dollar deficits returning by 2022.
- Debt held by the public (on which interest is paid) will grow by $11.2 trillion between now and 2027, from $14.3 trillion today.
- Spending will grow from 20.9 percent of GDP in 2016 to 23.6 percent in 2027, while revenues will rise from 17.8 percent in 2016 to 18.4 percent by 2027.
- The vast majority of spending growth over the next decade (83%) is the result of rising costs for health care, Social Security, and interest on the debt.
Conclusion. The national debt is growing much too fast. The only way to turn this dangerous situation around is to reform all entitlement programs, including Medicaid, to get their costs under much better control.
Follow me on Twitter: https://twitter.com/jack_heidel
Follow me on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/jack.heidel.3