I have now been writing this blog for four years, beginning right after the presidential election of 2012. I was a candidate in the May 2012 Republican Primary for the 2nd Congressional District of Nebraska. I campaigned on the platform to “eliminate the deficit.” I lost to the incumbent Lee Terry who was in turn replaced in office by the Democrat Brad Ashford in 2014.

The overriding theme of my blog is “how to restore fiscal responsibility to our national government.” I discuss two fundamental and related issues:
- Massive Debt now 75% of GDP, the highest level since right after WWII, and predicted by the Congressional Budget Office to keep rising steadily under current policies.
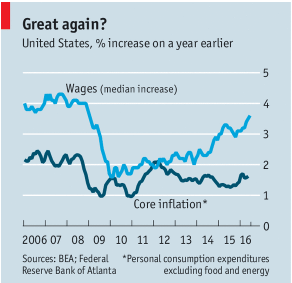
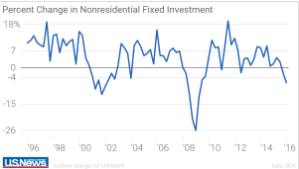
- Slow Economic Growth averaging just barely 2% per year since the end of the Great Recession in June 2009. Although the unemployment rate is down to a respectable 4.9%, the labor participation rate is also lower than usual. Faster growth would mean more jobs and better paying jobs. It would also mean more tax revenue to shrink our annual deficits.
How should these problems be addressed? In briefest outline:
- Balanced Budget Amendment to the Constitution. This is a drastic measure but I see no other way to get the job done. The pressure on Congress is always to create new programs and spend more money, not less. A BBA could be designed in a flexible manner to allow emergency overrides. It could also be phased in by, for example, having an effective date three years after ratification. It so happens that 28 states (out of 34 needed) have now called for a Constitutional Convention to propose such an amendment. (http://bba4usa.org/)
- Tax Reform, lowering rates for individuals and corporations, paid for by shrinking deductions, would do wonders for encouraging business investment and entrepreneurship, as well as encouraging American multinational companies to bring their foreign earnings back home for reinvestment.
Conclusion. Much more can be done but this would be a very good start.