As my regular readers know I am focused primarily on two major national problems:
- Speeding up economic growth to create more jobs and better paying jobs, and
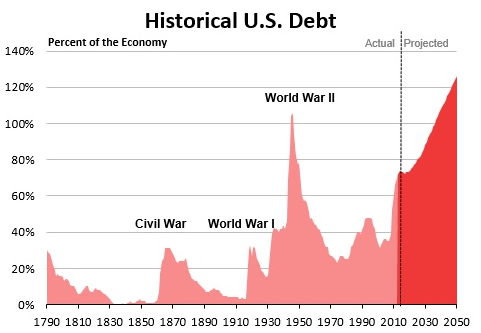
- Getting our national debt under control by reducing our annual budget deficits so that our debt will shrink over time as a percentage of GDP.
The evidence continues to persuade me that entitlement spending in general and the cost of healthcare in particular will play the biggest role in solving these two problems. My last post points out that healthcare, higher education and housing are all drags on family expenses but that the cost of healthcare has by far the largest negative effect on our economy.
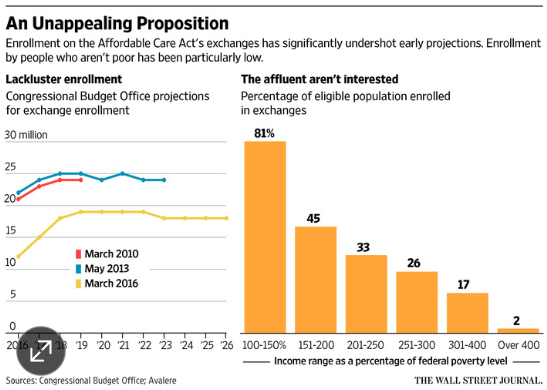
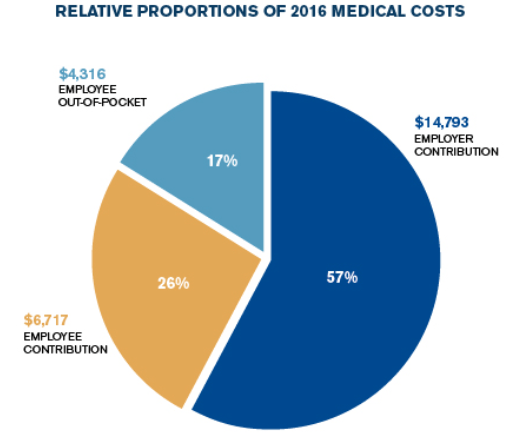
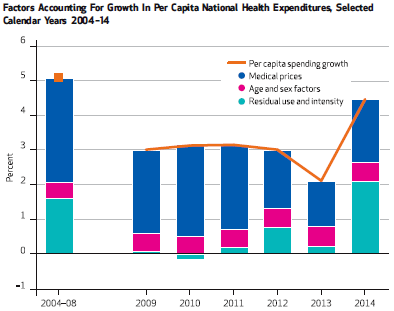
The United States spends 18% of GDP (and climbing) on healthcare, both public and private, twice as much as any other developed country. This enormous expense must be reduced but how will it happen? The Affordable Care Act has increased access to healthcare but has not bent the cost curve.
Now the Republicans (President-elect Trump and Congress) want to repeal the ACA and replace it with something less restrictive and less expensive. A popular alternative is health insurance which has:
- High deductibles typical of catastrophic coverage in order to hold down the cost of insurance.
- Tax credits to defray the cost of insurance.
- Tax preferred health savings accounts to pay for routine expenses below the deductible.
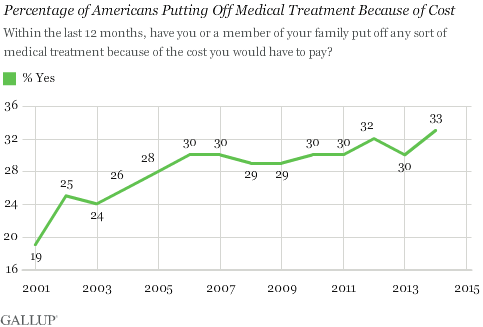
Unfortunately it’s not this simple. Today’s New York Times has a credible Op Ed by Drew Altman, CEO of the Henry Kaiser Family Foundation, “The Health Care Plan Trump Voters Really Want,” which reports on a series of focus groups set up by Kaiser after the election to quiz Trump voters about healthcare. What Kaiser learned about Trump voters is that:
- In the pre-ACA market, they liked their ability to buy lower-cost plans which met their needs.
- They want lower drug costs and improved access to cheaper drugs.
- The very last thing they want in healthcare reform is higher out-of-pocket costs.
Conclusion. What Trump voters are looking for in healthcare reform is quality healthcare at a low cost. This is also the Republican ideal. But the high deductible plus health savings account combination is going to be a hard sell to many Trump voters.
Follow me on Twitter
Follow me on Facebook