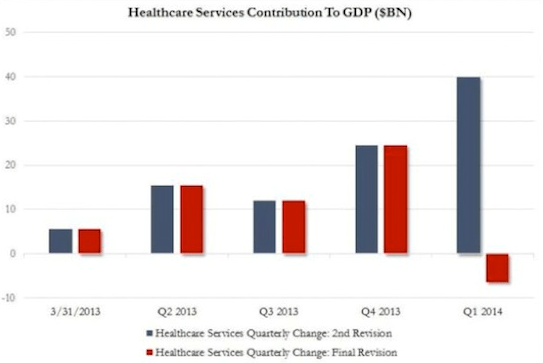
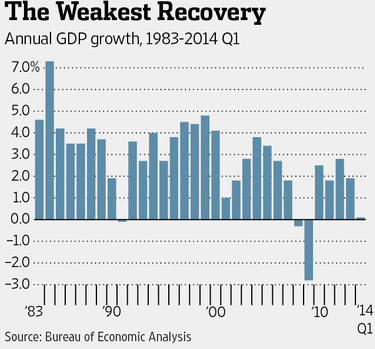
The Washington Post reporter Robert Samuelson gives our economy today a B-, because the unemployment rate has inched down to 6.1%, fulltime employment is up to 105.8 million in 2013 from 99.5 million in 2010, and full-time women’s pay reached a high of 78% of men’s pay in 2013. The big negative, of course, is that median household income was $51,939 in 2013, down from $56,436 in 2007, just before the financial crisis.
The Bard College economist Pavlina Tcherneva, as summarized by the reporter Neil Irwin in yesterday’s New York Times, shows what has gone wrong with economic and monetary policy since the end of the Great Recession in June 2009. The American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 (an $850 billion stimulus package) did boost the economy but it primarily aided “the skilled, employable, highly educated, and relatively highly-paid wage and salary workers.”
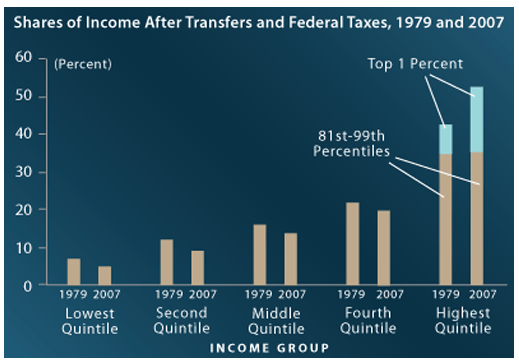
 On the other hand the Federal Reserve’s quantitative easing policies have kept interest rates remarkably low and have thereby caused investors to buy stocks rather than bonds in order to get higher returns. This has artificially boosted stock prices and has been especially advantageous to the top 10% and, even more so, the top 1%.
On the other hand the Federal Reserve’s quantitative easing policies have kept interest rates remarkably low and have thereby caused investors to buy stocks rather than bonds in order to get higher returns. This has artificially boosted stock prices and has been especially advantageous to the top 10% and, even more so, the top 1%.
 What is needed, according to Ms. Tcherneva, is a targeted, bottom-up approach to fiscal policy, which provides more and better paying jobs directly to middle- and lower-income wage earners. Her suggestion is for public works jobs, public service employment, green jobs, etc., all of which would require large infusions of federal money thereby worsening the federal deficit.
What is needed, according to Ms. Tcherneva, is a targeted, bottom-up approach to fiscal policy, which provides more and better paying jobs directly to middle- and lower-income wage earners. Her suggestion is for public works jobs, public service employment, green jobs, etc., all of which would require large infusions of federal money thereby worsening the federal deficit.
A much better approach would be broad based tax reform, lowering tax rates across the board, paid for by closing the loopholes and deductions which primarily benefit the rich. Since the 64% of taxpayers who do not itemize deductions would receive an effective pay boost, this would amount to a tax reform program targeted to exactly the middle- and low-income wage earners who have not yet recovered from the recession. These folks would most likely spend their extra income, thus further boosting the economy (see my previous post).