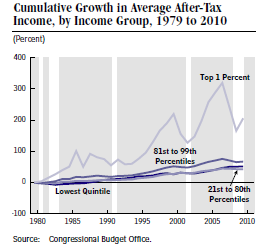
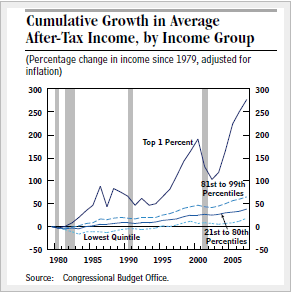
In yesterday’s New York Times an editorial asks the question “Where Have All the Raises Gone?”, pointing out that wages for college graduates have been stagnant since 2001 (see the chart below.) A report referred to in the NYT editorial suggests that as the information technology revolution has matured, employer demand for cognitive skills has waned and so some college graduates have had to take lower paying jobs, displacing less educated lower skilled workers in the process. This makes sense and, of course, new hiring has slowed down even more as a result of the recession.
 The question then becomes, what, if anything can government do to counteract and overcome this trend? According to the NYT, “what’s needed to raise pay are policies like a higher minimum wage, trade pacts that foster high labor and regulatory standards, and more support for union organizing.”
The question then becomes, what, if anything can government do to counteract and overcome this trend? According to the NYT, “what’s needed to raise pay are policies like a higher minimum wage, trade pacts that foster high labor and regulatory standards, and more support for union organizing.”
Of course there is another point of view and it is expressed very well in yesterday’s Wall Street Journal by Mortimer Zuckerman, the Chairman and Editor-in-chief of U.S. News and World Report, “Fight Inequality With Better Paying Jobs”. Mr. Zuckerman declares that “income inequality isn’t so much the problem as income inadequacy. A more robust economy, stoked by growth-oriented policies from Washington, would help produce the jobs and opportunities that millions of Americans need to climb the economic ladder.” He suggests that what is needed is:
- Lower corporate tax rates so that American multinational companies will bring their foreign earnings back home.
- Get healthcare costs under control (Obama Care doesn’t do this).
- Cut back on unnecessary regulations to encourage more business investment.
- Train more skilled workers. The National Federation of Independent Businesses reports that 38% of its members have job openings they can’t fill.
- Restore H1-B visa levels to the higher levels of earlier years – 195,000 per year compared to only 65,000 today. Skilled immigrants start many new businesses and this is the biggest source of new job creation.
In other words there are lots of things the federal government can do to boost the economy. As Mr. Zuckerman says, “The political system is failing us. Washington doesn’t seem to be listening as our political parties are focused more on ideological conflict than the good of the country.”