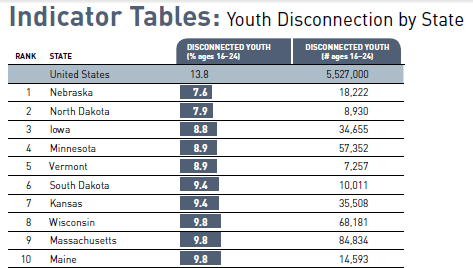
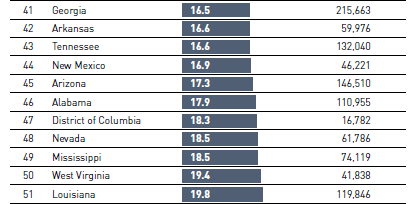
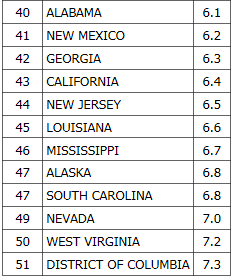
As we celebrate the 239th anniversary of the signing of the Declaration of Independence in 1776, Americans have much to be thankful for. It is often said that the United States is the strongest, wealthiest and freest country the world has ever known. Although this may be somewhat of an exaggeration (see below), it is still indicative of how fortunate we are compared to the rest of the world.
 As we celebrate our good fortune, we need to be acutely aware that our continued success as a great nation is not automatically assured. In fact we face a number of troubling and persistent problems which are not likely to disappear unless we take strong action to address them. For example we have:
As we celebrate our good fortune, we need to be acutely aware that our continued success as a great nation is not automatically assured. In fact we face a number of troubling and persistent problems which are not likely to disappear unless we take strong action to address them. For example we have:
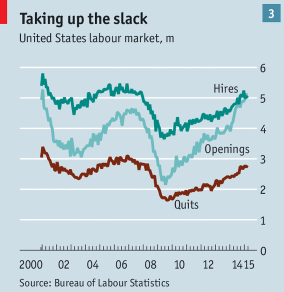
- A stagnant economy with only 2.2% annual growth since the end of the Great Recession. And the Congressional Budget Office predicts no speed up over at least the next ten years, based on current policy. Such slow growth condemns 20 million unemployed and underemployed citizens to unfulfilling lives, as well as lackluster pay raises for many more tens of millions.
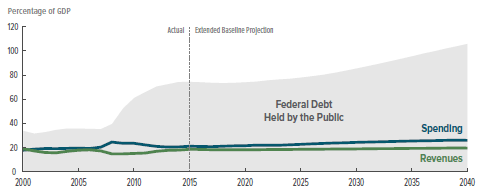
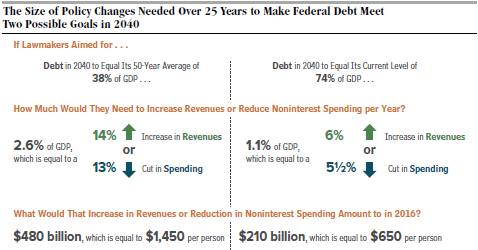
- Massive debt. Our public debt (on which we pay interest) is now at 74% of GDP, highest since the end of WWII, and predicted by the CBO to grow rapidly under current policies. When interest rates return to the normal 5% level, interest payments on the debt will skyrocket, making it much more difficult to fund all of the federal programs we depend on for our quality of life.
- Increasing Income Inequality is real even if overhyped in the media. America is still a land of great opportunity but basic fairness demands that all citizens be able to share in our national abundance.
- Threats from abroad. ISIS now controls much of Iraq, Syria and northern Africa and must be defeated. NATO needs our very strong support, all the more so with the Eurozone and European Common Market under increasing pressure from within.
As the strongest nation in the world we have much responsibility for continued world peace and prosperity. We can’t fulfill this role adequately unless our own internal fiscal and economic policies are in fundamentally sound shape.
Let’s be thankful for what we have and bear down hard to insure that we keep it!