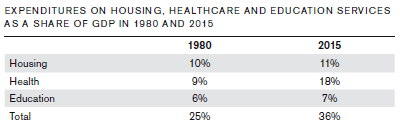My last post, “What Is Slowing Down the U.S. Economy,” reports on an interesting analysis by the Gallup economist, Jonathan Rothwell, making an excellent case that three of the biggest drags on the U.S. economy are the costs of:
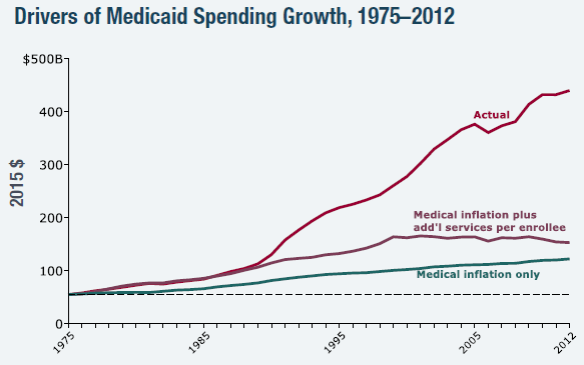
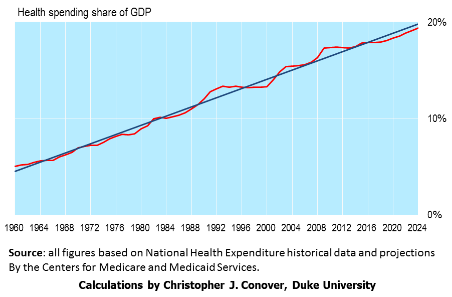
- Healthcare. By far the biggest drag, healthcare costs have increased from 9% of GDP in 1980 to 18% in 2015. Mr. Rothwell notes that the average U.S. physician spends $83,000 per year to process claims and interact with insurance companies compared to $22,000 in Canada which has a single payer system. The solution, in my opinion, is to change the tax treatment of employer provided health insurance (to cover catastrophic coverage only) in order to give individuals more “skin in the game.”
- Education. Although education costs have risen only from 6% to 7% of GDP over the past 35 years, education overall is 8.9% more expensive in 2015 than in 1980 and higher education is 11.1 times more expensive. Considering the ever increasing need for highly trained workers in today’s high-tech and globally competitive economy, such rapidly increasing cost presents a huge impediment to progress. Foundational K-12 education is also failing to close the achievement gap between low-income minority students and middle-class students. Such disparity in educational outcomes bodes ill for future social harmony. Even overall cognitive performance in math and literacy is now declining (see chart). These are tough problems to solve.
- Housing. Again, only a 1% increase (from 11% to 12%) in GDP from 1980 to 2015 but this translates into a rental cost increase of 19% of GDP in 1980 to 28% of GDP in 2015. Also mortgage payment costs increased from 12% of GDP in 1980 to 16% of GDP today. Mr. Rothwell attributes these increases to a tightening of local zoning restrictions. There does not appear to be any general policy solution to such a problem.
Conclusion. The costs of healthcare, education and housing are eating up greater and greater amounts of family income and therefore are retarding economic growth and social progress. What can be done about these problems? Stay tuned!