I am a fiscal conservative, as well as a social moderate, which means that I don’t fit very easily into a standard mold. I am non-doctrinaire, non-ideological and mostly nonpartisan. I vote for candidates from both major parties as well as independents. I prefer a balanced government with neither party in complete control.
My most direct sources of information on fiscal and economic issues are the Wall Street Journal and the New York Times, both of which I read assiduously on a daily basis. When these two newspapers disagree on a particular issue, then I usually decide that the truth lies somewhere in between.
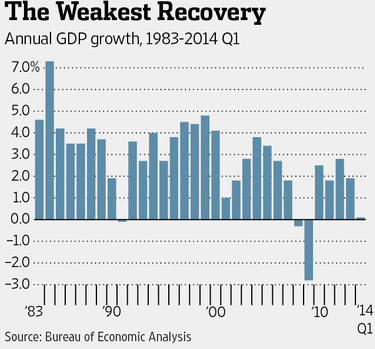 Our biggest national problem right now, in my opinion, is the stagnant economy. In today’s WSJ, the lead editorial, “The Growth Deficit”, clearly describes how bad the situation is. Since the Great Recession ended in June 2009, our rate of GDP growth has averaged 2.2% per year. This compares with a 4.1% annual rate of growth for all post-1960 recovery periods.
Our biggest national problem right now, in my opinion, is the stagnant economy. In today’s WSJ, the lead editorial, “The Growth Deficit”, clearly describes how bad the situation is. Since the Great Recession ended in June 2009, our rate of GDP growth has averaged 2.2% per year. This compares with a 4.1% annual rate of growth for all post-1960 recovery periods.
Such a slow rate of growth causes all sorts of problems. First of all, it explains why our unemployment rate is still so high at 6.7% after five years of recovery. This means that between 15 and 20 million people are still unemployed or underemployed. Such a large human toll means a huge increase in government welfare expenses for food stamps, unemployment insurance, etc. Higher unemployment also means less tax revenue collected by the federal government. This translates into much larger deficit spending, adding to the already massive national debt.
There are lots of things which can be done to increase growth, for example:
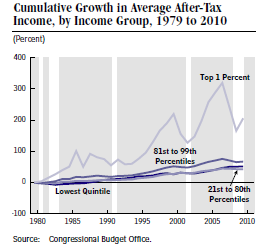
- Lowering tax rates on individuals to put more money in the hands of the 2/3 of Americans who do not itemize deductions on their tax returns. They’ll spend this extra income and create more demand! Pay for this by closing loopholes and deductions, which are used primarily by the wealthy. Besides stimulating the economy, this will simultaneously address increasing income inequality.
- Lowering tax rates on corporations to encourage multinationals to bring their foreign profits back home for reinvestment or paying dividends. Again, balanced by eliminating deductions enjoyed by privileged corporations.
- Relax regulatory burdens on small businesses where most new jobs are created.
- Reform immigration procedures by boosting the number of H1-B visas to attract more highly skilled, and entrepreneurial, foreign workers.
- Grant trade promotion authority to the President to speed up new trade agreements.
We should be clamoring for our national leaders to be acting on these fronts. A strong economy is the very backbone of our success as a nation!