In my last post I said that Donald Trump won the first presidential debate, in spite of his uneven temperament, because he was more correct on the issues.
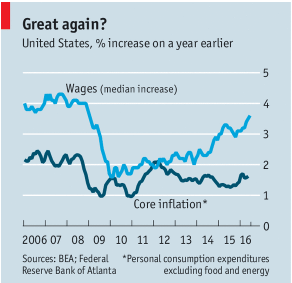
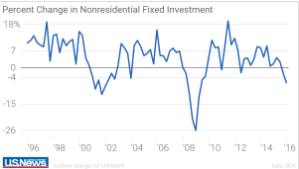
One of the biggest problems our country faces is slow economic growth, averaging only 2% per year since the end of the Great Recession in June 2009. This compares with an average rate of growth of 3.5% from 1950 – 2000.
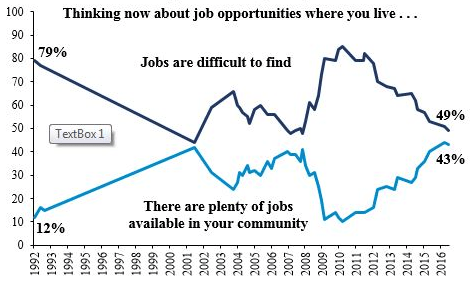
In fact, even the recent job growth we have seen is now leveling off.
 Such slow growth is very dangerous long term for many reasons:
Such slow growth is very dangerous long term for many reasons:
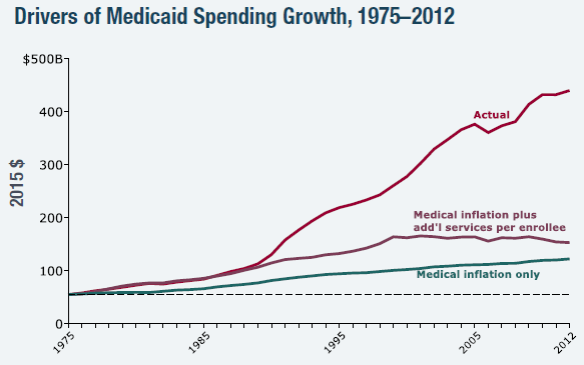
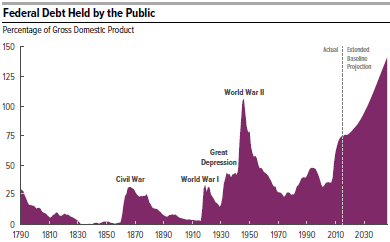
- Massive Debt. Our public debt, on which we pay interest, is now 75% of GDP, the highest it has been since right after WWII. CBO predicts that this percentage will keep getting steadily worse without major policy changes. Faster growth means more tax revenue and therefore smaller annual deficits. It is imperative to put our accumulating debt on a downward path.
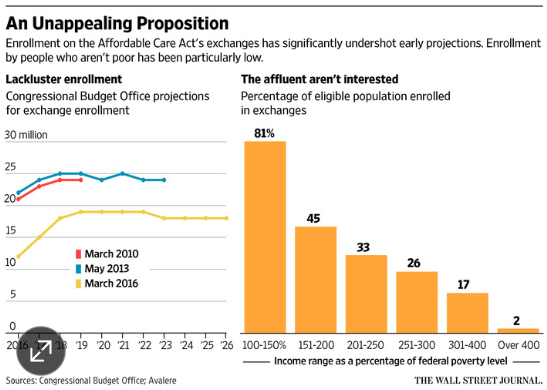
- The Need for More Jobs and Better Paying Jobs. The best way to achieve broad based prosperity, and minimize populist disruption, is to create a tight job market where employers have to compete for employees. This is accomplished by making the economy grow faster.
- Keeping Ahead of China. In 2009 China’s economy was 1/3 the size of ours; now it is 60% as big. In other words, China will soon surpass us economically if we are unable to grow faster. This would risk losing our worldwide lead in such crucial areas as new technology and financial depth, as well as our superpower status.
- Reducing Student Loan Debt. The best way we can help former students pay off their college debt is to have good jobs waiting for them when they leave school. The faster our economic growth, the better we can do this.
Conclusion. Both our own individual success in life as well as the overall status of our nation depends upon the availability of opportunity. This is why economic growth is so important and why it is dangerous to let it lag.