“As for the future, your task is not to foresee it, but to enable it.”
Antoine de Saint-Exupery, 1900 – 1944
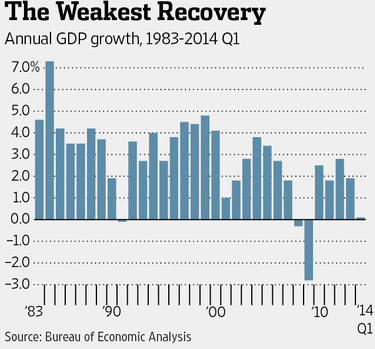
An important new book, “Dead Men Ruling,” by the Urban Institute’s C. Eugene Steuerle, has just been published. Here is the flavor of its message:
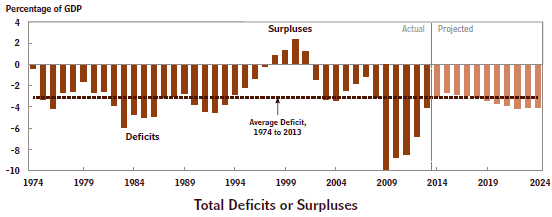
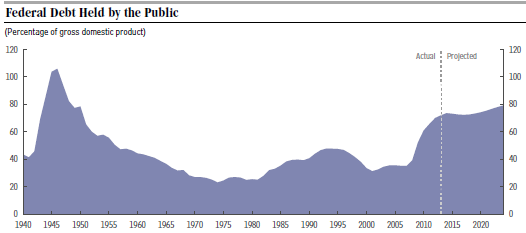
 “Dead and retired policymakers have put America on a budget path in which spending will grow faster than any conceivable growth in revenues. … The same policy makers also cut taxes so much below spending that they created huge deficits, which have now compounded the problem with additional debt.”
“Dead and retired policymakers have put America on a budget path in which spending will grow faster than any conceivable growth in revenues. … The same policy makers also cut taxes so much below spending that they created huge deficits, which have now compounded the problem with additional debt.”
“Both sides have largely achieved their central policy goals – liberals have expanded social welfare programs, conservatives have delivered lower taxes. Both now cling tenaciously to their victories.”
In short, “our central problem is the loss of fiscal freedom.” There are “four deadly economic consequences of this disease:
- rising and unsustainable levels of debt,
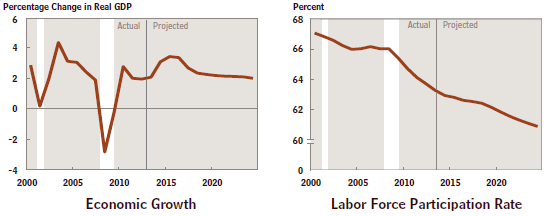
- shrinking ability of policymakers to fight recession or address other emergencies,
- a budget that invests ever less in our future and is now a blueprint for a declining nation, and
- a broken government, as reflected in antiquated tax and social welfare systems.”
In addition there are “three deadly political consequences:
- a decline of ‘fiscal democracy’ depriving current and future voters of the right to control their own budget,
- a classic ‘prisoner’s dilemma’ where both left and right leaning elected officials conclude that they will suffer politically if they lead efforts to impose either spending cuts or tax hikes, and
- rising hurdles to changing our fiscal course because, to do anything new, requires reneging on past promises of rising benefits and low taxes, that voters have come to expect.”
In other words the U.S. is in a very difficult predicament. Mr. Steuerle thinks it will take a major “fiscal turning point” to escape from the present danger. Both sides will have to make big concessions in order for us to get out of this jam. But how is this possibly ever going to happen? More next time!