The Congressional Budget Office has just issued the report ”The Budget and Economic Outlook: 2014 to 2024”, giving its usual objective and nonpartisan look at our prospects for the next ten years. My purpose today is to give a simple interpretation of its basic data. In my next post I will address the implications of this interpretation.
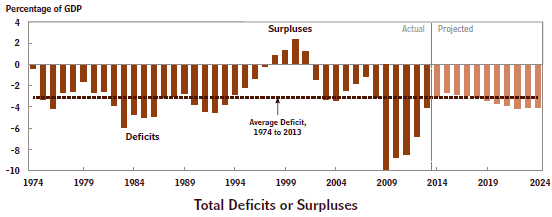
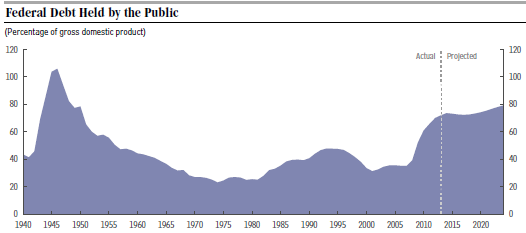 The first chart above shows a forty year history of government deficit spending. The average deficit for this time period is 3% of GDP. From 1982 – 1987 the deficits were worse than this and from 2009 – 2013 they were much worse. The real problem is the accumulated deficits, i.e. the debt. The second chart above shows the public debt (what we pay interest on) all the way back to 1940 as a percent of GDP. As recently as 2008, the public debt was below 40% of GDP. Now it is 73% and climbing. This is very serious for two reasons. Right now our public debt is almost free money because interest rates are so low. But when interest rates return to their normal level of about 5%, interest payments will explode and be a huge drain on the economy. In addition, these CBO predictions assume continued steady growth of the economy. If and when we have a new recession or some other financial crisis, there will be much less flexibility available for dealing with it.
The first chart above shows a forty year history of government deficit spending. The average deficit for this time period is 3% of GDP. From 1982 – 1987 the deficits were worse than this and from 2009 – 2013 they were much worse. The real problem is the accumulated deficits, i.e. the debt. The second chart above shows the public debt (what we pay interest on) all the way back to 1940 as a percent of GDP. As recently as 2008, the public debt was below 40% of GDP. Now it is 73% and climbing. This is very serious for two reasons. Right now our public debt is almost free money because interest rates are so low. But when interest rates return to their normal level of about 5%, interest payments will explode and be a huge drain on the economy. In addition, these CBO predictions assume continued steady growth of the economy. If and when we have a new recession or some other financial crisis, there will be much less flexibility available for dealing with it.
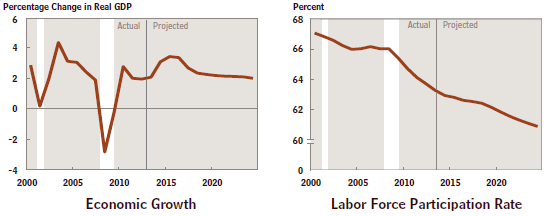 Now look at the last two charts. The first one shows the rate of GDP growth since 2000 which has averaged about 2% since the end of the recession in June 2009 and is projected by the CBO to level off at this same rate over the next 10 years. This is an historically low rate of growth for our economy. The final chart shows the gradual decrease of the labor force participation rate over this same time period. These two graphs are related! When fewer people are working, the economy simply will not grow as fast.
Now look at the last two charts. The first one shows the rate of GDP growth since 2000 which has averaged about 2% since the end of the recession in June 2009 and is projected by the CBO to level off at this same rate over the next 10 years. This is an historically low rate of growth for our economy. The final chart shows the gradual decrease of the labor force participation rate over this same time period. These two graphs are related! When fewer people are working, the economy simply will not grow as fast.
High debt and slow growth are big problems for an economy. We’re falling more deeply into this perilous state of affairs all the time. We need to take strong measures to break out of this dangerous trap!

