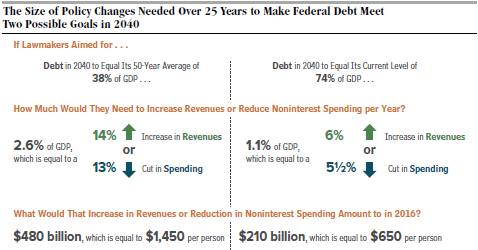
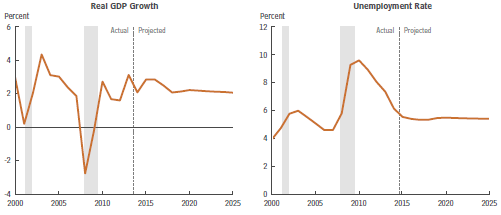
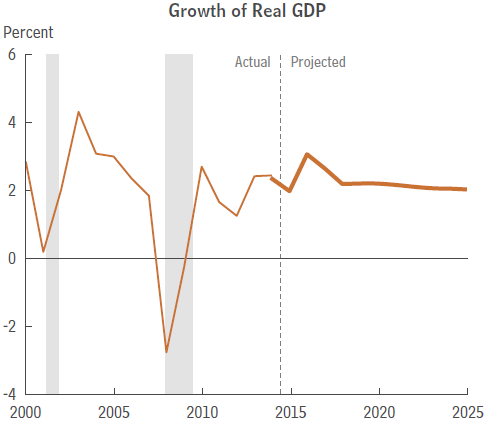
We have very high debt and Paul Krugman says in “Debt Is Good” that we need more! The Congressional Budget Office’s latest report this week, “An Update to the Budget and Economic Outlook: 2015 – 2025” predicts slow economic growth for the next ten years, averaging 2.1% per year (see chart below).
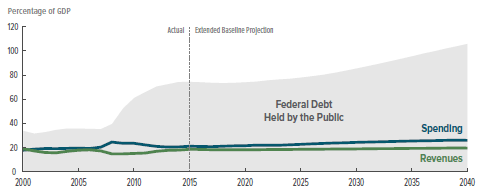
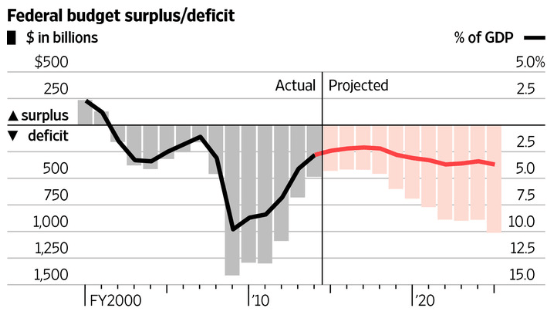
 Unfortunately, high debt and slow growth are a deadly, self-reinforcing, combination. Today’s Wall Street Journal has a chart (pictured below) showing clearly how budget deficits are likely to increase over the next ten years. The public debt (on which we pay interest) is predicted to grow from 74% of GDP today to 77% of GDP in 2025, increasing by a total of $7 trillion over this time period.
Unfortunately, high debt and slow growth are a deadly, self-reinforcing, combination. Today’s Wall Street Journal has a chart (pictured below) showing clearly how budget deficits are likely to increase over the next ten years. The public debt (on which we pay interest) is predicted to grow from 74% of GDP today to 77% of GDP in 2025, increasing by a total of $7 trillion over this time period.
 Here is another connection between slow growth and high debt:
Here is another connection between slow growth and high debt:
- Slow Growth means higher than necessary unemployment and under-employment as well as minimal raises for employed workers. The resulting economic slack leads to
- Low Inflation. But low inflation means that the Federal Reserve can maintain
- Low Interest Rates to try to encourage more borrowing to stimulate the economy. This means, in turn, that Congress can run up huge deficits without having to pay much interest on this almost “free” money. This eventually leads to:
- Massive Debt. But what happens when inflation does take off, which has happened before and is likely to happen again? Then the Federal Reserve is forced to raise interest rates quickly and we are stuck with huge interest payments on our accumulated debt. And meanwhile entitlement spending on Social Security, Medicare and Medicaid is also growing rapidly. At this point debt increases very rapidly which leads to a severe
- Fiscal Crisis.
Of course things don’t have to happen like this. Congress might become more responsible and either cut spending and/or raise taxes and start shrinking our huge deficits. Or perhaps slow growth really is the new normal and interest rates will remain low indefinitely. But slow growth is not pain free; there are many millions of unemployed and under-employed Americans who want to work and whose lives are stunted otherwise.
Slow growth is a very destructive path to be following. We badly need to adopt policies to speed it up!