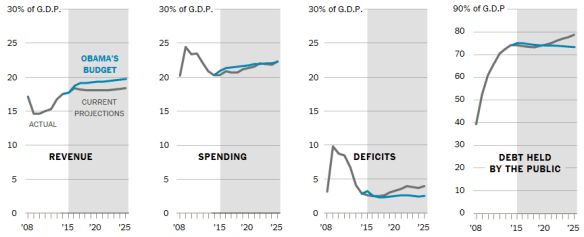
The unemployment rate in Nebraska is now down to 2.9% and even in Omaha, a relatively large metropolitan area of 850,000, it is only 3.2%. As reported by the Omaha World Herald today, such a low unemployment rate creates big problems for employers at all levels.
 For example:
For example:
- In fast foods, beginning salaries are up to $10 or more per hour, well above Nebraska’s new minimum wage of $8 per hour, and raises for responsible employees are frequent. Manager’s salaries are increasing rapidly. Benefits are being expanded into such areas as tuition reimbursement.
- For the predominantly minority residential area of North Omaha, with a traditional unemployment rate of up to 20%, local manufacturers are beginning to provide transportation vans to pick up and drop off workers.
- The Omaha Chamber of Commerce is running an ad campaign in Seattle to appeal to soon-to-be-laid-off Microsoft workers, because there are lots of vacant tech positions in Omaha.
- Both the Greater Omaha Chamber of Commerce and the Lincoln Chamber of Commerce have endorsed LB 586 in the Nebraska Legislature to ban discrimination in the workplace based on sexual orientation and gender identity. The purpose, as expressed by both chambers of commerce, is to create a more attractive work environment in order to attract more workers from other states. The neighboring states of Iowa and Colorado have passed such laws.
What more can be done? The welcoming labor market should provide a bigger incentive for both high school and college students to finish their studies and graduate. Jobs will be waiting for them! The labor shortage should also help create more interest in immigration reform. This would insure that Nebraska has an adequate number of legal guest workers to meet the needs of the agricultural and meatpacking industries.