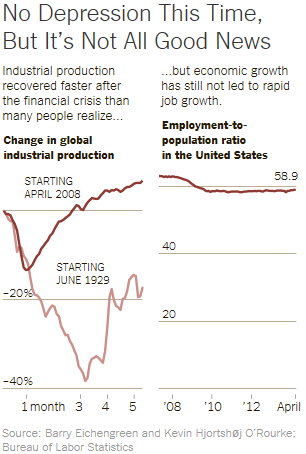
The publication of two new books is causing a reevaluation of the financial rescue and its aftermath, e.g. “The Case Against the Bernanke-Obama Financial Rescue”. The two books are “Stress Test” by Timothy Geithner, former Treasury Secretary, and “House of Debt” by the economists Atif Mian and Amir Sufi.
 Mr. Mian and Mr. Sufi maintain that the government’s response to the financial crisis should have focused less on saving the banking system and more on the problem of excessive household debt. They discovered in their research that, during the housing bubble, less affluent people were spending as much as 25 – 30 cents for every dollar of increase in housing equity. When the bubble burst, and housing prices started to fall, these borrowers cut way back on spending which caused many businesses to lay off employees. The authors propose setting up a government program to help borrowers decrease what they owe in underwater mortgages.
Mr. Mian and Mr. Sufi maintain that the government’s response to the financial crisis should have focused less on saving the banking system and more on the problem of excessive household debt. They discovered in their research that, during the housing bubble, less affluent people were spending as much as 25 – 30 cents for every dollar of increase in housing equity. When the bubble burst, and housing prices started to fall, these borrowers cut way back on spending which caused many businesses to lay off employees. The authors propose setting up a government program to help borrowers decrease what they owe in underwater mortgages.
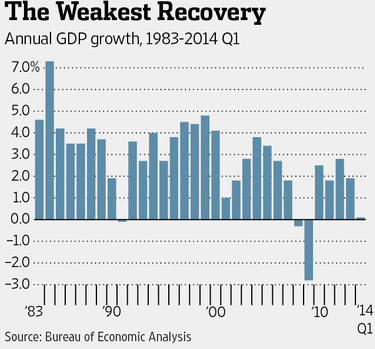
Five years after the end of the Great Recession it would still be very helpful to speed up our lagging economy. Here are three different possible ways to do this:
- The Keynesians say the best way to stimulate the economy is with more government (deficit) spending. For example, spending several hundred billion dollars a year on infra-structure would create hundreds of thousands, if not millions, of new construction jobs. I think this is a good idea, but only if it’s paid for with a new tax (e.g. a carbon tax or a wealth tax).
- The Mian/Sufi plan, as described above, would alleviate mortgage debt problems for millions of middle class homeowners who are still under water, encouraging them to spend more money which would in turn boost the economy. The problem is that the M/S plan creates a moral hazard for mortgage holders unless it’s paid for by mortgage insurance which would raise costs for borrowers.
- Broad-based tax reform, with lower tax rates for everyone, paid for by closing loopholes and limiting tax deductions for the wealthy, would automatically put more income in the hands of the two-thirds of tax payers who do not itemize deductions. These middle class wage earners would tend to spend this extra money thereby boosting the economy.
The point is that there very definitely are ways to boost the economy, some better than others, and it should be a top priority of Congress and the President to get this done.