The federal Highway Trust Fund is almost out of money. It takes in $35 billion per year from the 18.4 cents per gallon federal gas tax, which has not been raised since 1993. Sometime this summer the government will have to cut back on payments to state highway departments unless Congress acts.
 As the above chart from the Economist shows, the U.S. spends much less of GDP on roads than many other developed nations. Something clearly needs to be done because we need many improvements in infrastructure. But there are better ways and poorer ways to solve this problem. Here are two good ways as described by Thomas Donlan in a recent issue of Barron’s:
As the above chart from the Economist shows, the U.S. spends much less of GDP on roads than many other developed nations. Something clearly needs to be done because we need many improvements in infrastructure. But there are better ways and poorer ways to solve this problem. Here are two good ways as described by Thomas Donlan in a recent issue of Barron’s:
- A bill to raise the gas tax by 12 cents per gallon over two years has been introduced in the Senate by Bob Corker (R, Tenn.) and Chris Murphy (D, Conn.). Each penny added to the federal gas tax rate will raise $1.3 billion and this would solve the problem.
- Repeal the federal gas tax and turn federal highway construction entirely over to the states. Each state could then increase its own gas tax and/or pay for construction with tolls on bridges and roads.
Here are two examples of poor ways to replenish the Highway Trust Fund:
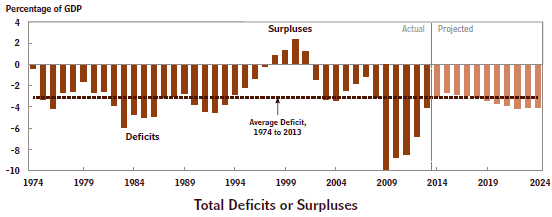
- Continue adding to the Fund with borrowed money. $54 billion has been borrowed since 2008 for this purpose. Presumably the Sequester will make it much harder to continue such deficit financing.
- Rep John Delaney (D, Mary.) has proposed a tax break for repatriated foreign profits by multinational American companies if part of the money brought back was spent on infrastructure bonds. This would interfere with the urgent need to reform corporate taxes with significantly lower rates offset by lowering deductions, in order to make our corporate tax internationally competitive.
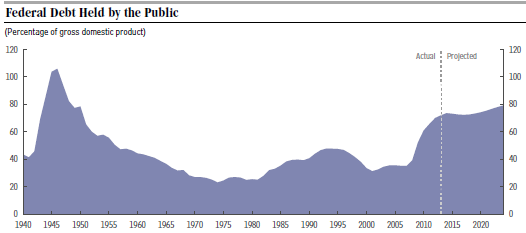
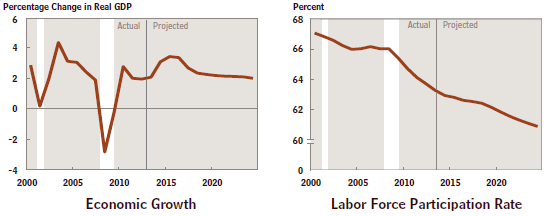
Conclusion: There is a good chance that the Budget Sequester established by Congress in 2011 to control discretionary spending, as well as the widely recognized urgent need for corporate tax reform, will lead to a “good” rather than “bad” solution to the shortfall in the Highway Trust Fund. This is just one specific example of the challenge to sensible budgeting by Congress.
A much broader approach is needed to really shrink the deficit. Stay tuned!