My last two posts have been devoted to discussing the prospects for a true free-market healthcare system in the U.S. Let’s bring this discussion down to earth with two specific examples.
 In Omaha NE, where I live, there are three major hospital systems and one of them, Catholic Health Initiatives, is 30% more expensive than the other two. The major insurer, Blue Cross Blue Shield, has reacted by canceling its contract with CHI, making it out-of-network for Blue Cross policy holders.
In Omaha NE, where I live, there are three major hospital systems and one of them, Catholic Health Initiatives, is 30% more expensive than the other two. The major insurer, Blue Cross Blue Shield, has reacted by canceling its contract with CHI, making it out-of-network for Blue Cross policy holders.
As reported in today’s Omaha World Herald, “Non-CHI health clinics, hospitals handling influx,” the Nebraska Medical Center and Methodist Hospital System are seeing a large influx of Blue Cross insured patients. This is exactly what has been expected to happen and will eventually put pressure on CHI to lower its prices in line with the other two hospital systems.
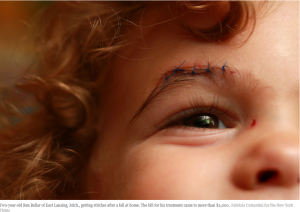
The second example, “Unable to Meet the Deductible or the Doctor” is the title of an article in yesterday’s New York Times. The article reports that 7.3 million Americans are now enrolled in insurance coverage through the Affordable Care Act. However the average deductible for a bronze plan on the exchange – the least expensive coverage – is $5,081 for an individual. This compares to the average deductible of $1,217 for individual coverage in employer-sponsored plans.
Not surprisingly, relatively low-income people obtaining subsidized coverage through an exchange are likely to want a low cost policy. But with a high deductible they will then be hard-pressed to have to pay the full price of routine care out of there possibly meager budgets. This is going to be a larger and larger problem as more and more people obtain coverage through the exchanges.
Since all of an individual’s medical bills should go through the insurer for processing, insurance companies are in a position to, and should be expected to, help control costs by bargaining with providers to make sure that prices are not excessive.
Conclusion: here are two examples of price competition in today’s healthcare market place. This is the reality that more and more Americans are going to have to learn to live with. It is the only way that our excessive healthcare costs can be brought under control.