My post on February 27, “A Breath of Fresh Air” praises the new tax reform proposal from the House Ways and Means Committee which both lowers and consolidates tax rates in a revenue neutral way as well as greatly simplifying the tax code. It would be a big step in the right direction. But the Washington Post’s Robert Samuelson makes a good case in ”Does Tax Reform Have a Future?” that the House bill does not go far enough.
 Mr. Samuelson argues that if we’re going to eliminate tax deductions and loopholes, and thereby alienate lots of special interest groups, in order to get lower tax rates, then we should avoid half measures and eliminate virtually all deductions in order to get the lowest possible rates. In other words, eliminate the mortgage interest deduction rather than just limiting it, eliminate deductions for charitable contributions as well as deductions for state and local taxes. Eliminate the deduction for employer provided healthcare (which by itself would go a long way towards reforming healthcare.)
Mr. Samuelson argues that if we’re going to eliminate tax deductions and loopholes, and thereby alienate lots of special interest groups, in order to get lower tax rates, then we should avoid half measures and eliminate virtually all deductions in order to get the lowest possible rates. In other words, eliminate the mortgage interest deduction rather than just limiting it, eliminate deductions for charitable contributions as well as deductions for state and local taxes. Eliminate the deduction for employer provided healthcare (which by itself would go a long way towards reforming healthcare.)
Mr. Samuelson would retain only the Earned Income Tax Credit (which encourages low-income people to work) and also the tax preference for contributions to retirement accounts (without which most Americans wouldn’t save for retirement.)
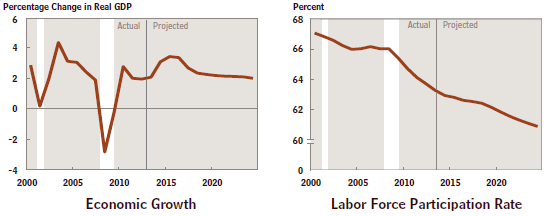
We badly need broad based tax reform to stimulate our economy. Douglas Holtz-Eakin, the former director of the Congressional Budget Office, has estimated “Reforming Taxes, Goosing the Economy”, that even the imperfect House tax reform proposal would raise GDP by .5% annually for 10 years and create 500,000 new jobs each year over this time period.
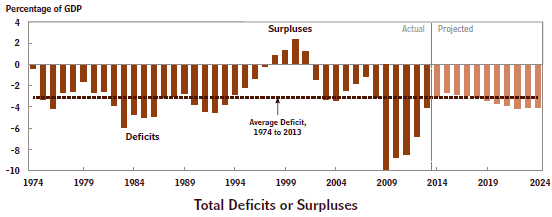
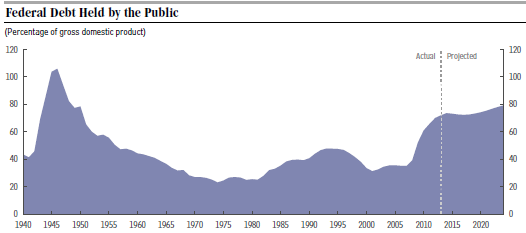
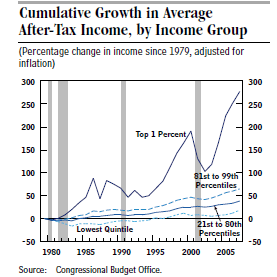
Full-fledged tax reform, a la Samuelson, would provide an even greater stimulus but let’s at least do something to put the millions of unemployed and underemployed people back to work and reduce our staggering budget deficits!