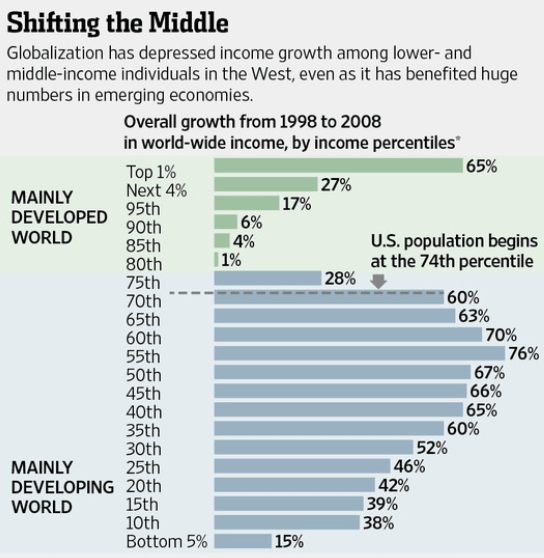
President Obama has proposed a $3.99 trillion budget for next year, a $340 billion increase from the current 2015 budget year. As shown in the charts below, it projects deficits of about 2.6% over the next ten years equal to its (optimistic in comparison to the CBO) growth projections for GDP. This means that the debt would stabilize at about 73% of GDP. And, of course, achieving his predicted stabilization of debt will require big tax increases over this ten year period.
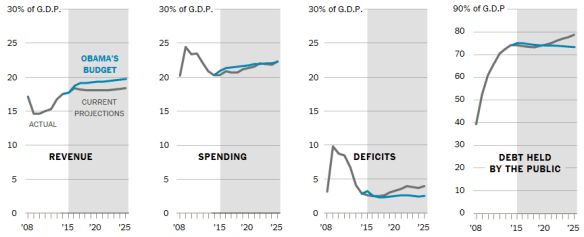 Here are the major weaknesses in the budget:
Here are the major weaknesses in the budget:
- Sequestration. The President declares that “I’m not going to accept a budget that locks in sequestration going forward.” Everyone deplores the mindlessness of sequestration but the only responsible alternative is to make targeted cuts throughout the budget. The President makes no attempt to do this. And he wants to add spending for various new education and research initiatives, as well as an expanded Earned Income Tax Credit for low-income workers.
- Infrastructure. Spending over the next six years would increase by $238 billion to be raised from a 14% repatriation tax on the $2 trillion in foreign earnings held overseas by American multinational corporations. The problem is that any repatriation tax should be tied in with overall corporate and business tax reform, exchanging lower tax rates in return for closing loopholes and deductions, in order to make U.S. business taxes competitive with those of other countries. Fundamental tax reform is the key to getting our economy growing faster.
- Entitlements. The President’s budget does not even mention the biggest threat to long-term fiscal sustainability, namely the rapidly increasing spending for Social Security, Medicare and Medicaid. It will be very difficult to make progress on this critical issue without presidential leadership.
- Stabilization of the Debt. The President’s budget, with quite optimistic revenue and growth projections, stabilizes the debt over ten years. But this is not nearly good enough. To be satisfied with a public debt of 73% of GDP indefinitely into the future is simply too risky. What’s going to happen when we have another financial crisis, as we surely will? How are we going to cope with our growing rivalry with China with very little budget flexibility? And one can imagine any number of other possible emergencies which might occur. Putting the debt on a clear downward trajectory is the only prudent thing to do!


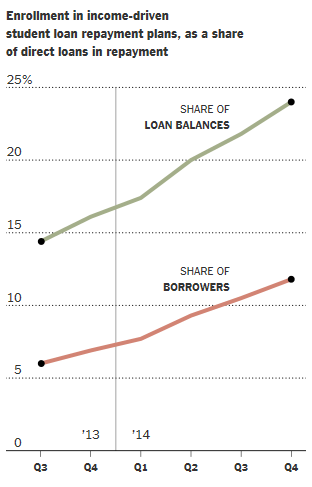



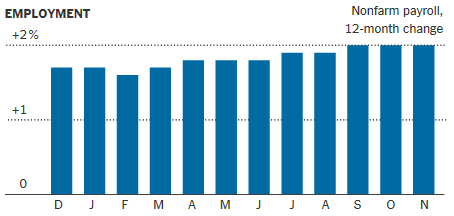 The New York Times predicts that the “
The New York Times predicts that the “