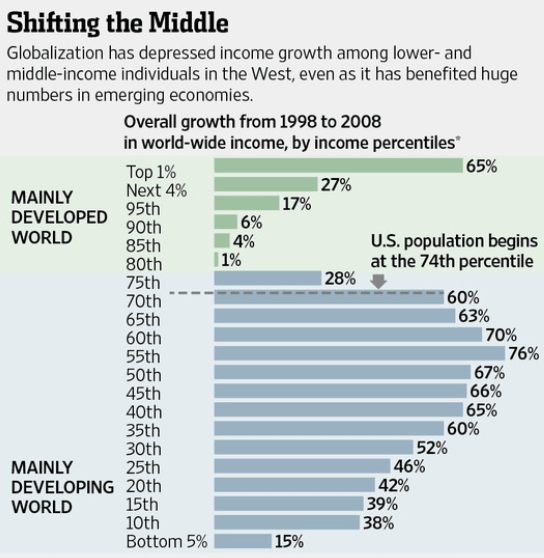
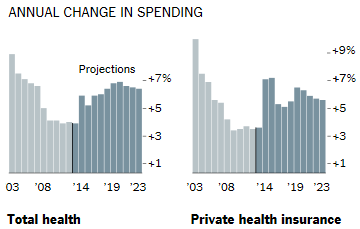
The New York Times has two recent articles about health care spending, “Good News inside the Health Spending Numbers” and “The Battle over Douglas Elmendorf – and the Inability to See Good News.” These two articles focus on the fact, clearly evident in the chart just below, that the rate of increase in overall health care spending has slowed down since 2009. In fact health care spending has been a constant 17.4% of GDP for the past four years, while it increased by 1.9% of GDP in the four years before that. More precisely, health care spending rose by 3.6% in 2013, down from 4.1% in 2012.
 It is, of course, very good news that increases in health care spending have dropped dramatically since the recession in 2007-2009, but is it really surprising that this has happened in the midst of so much economic pain, with a very high rate of unemployment as well as stagnant incomes for most Americans? In fact, even in these circumstances, health care spending is still growing at twice the rate of inflation, which has been under 2% during this same time period.
It is, of course, very good news that increases in health care spending have dropped dramatically since the recession in 2007-2009, but is it really surprising that this has happened in the midst of so much economic pain, with a very high rate of unemployment as well as stagnant incomes for most Americans? In fact, even in these circumstances, health care spending is still growing at twice the rate of inflation, which has been under 2% during this same time period.
A more realistic view of health care spending has just been presented to the Health Subcommittee of the House Committee on Energy and Commerce by Marc Goldwein, from the non-partisan Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget, a Washington D.C. think tank focused on fiscal responsibility. Mr. Goldwein makes the following points:
- Despite the recent slowdown in health care spending, it remains incredibly important that policymakers pursue reforms to reduce future projected health care costs.
- Policymakers should focus first and foremost on health care “benders” that would improve incentives in order to slow the overall growth of health care spending.
- Policymakers should next look to health cost “savers” which reduce federal costs by better allocating resources within the federal health programs.
- Given the aging of the population, health reforms will be necessary but not sufficient to put the debt on a sustainable long-term track.
Slowing down the rate of growth of health care is going to be a huge challenge for our national leaders. I will elaborate on how to do this in forthcoming blog posts.

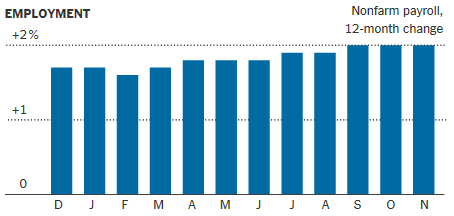 The New York Times predicts that the “
The New York Times predicts that the “