Our country faces two major fiscal and economic problems:
- How to boost the economy in order to put more people back to work.
- How to either increase tax revenue or better control spending in order to shrink the deficit.
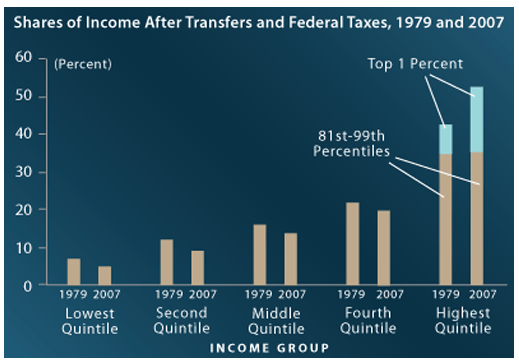
My last post, “The Great Wage Slowdown and How to Fix It” makes a specific tax reform proposal to cut tax rates for all by shrinking tax deductions for the wealthy. This would put tax savings in the hands of millions of wage earners with stagnant incomes, who would likely spend it, thereby boosting the economy.
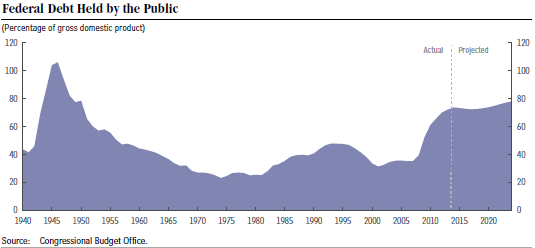
 As the above chart clearly shows, there is only one realistic way to shrink the deficit. We have to do a better job of controlling entitlement spending (Social Security, Medicare and Medicaid.) As a practical matter, this means we have to cut back the cost of American healthcare in general, both public and private.
As the above chart clearly shows, there is only one realistic way to shrink the deficit. We have to do a better job of controlling entitlement spending (Social Security, Medicare and Medicaid.) As a practical matter, this means we have to cut back the cost of American healthcare in general, both public and private.
The Manhattan Institute’s Avik Roy has come up with an attractive Plan for doing just this, “Transcending Obamacare.” Mr. Roy’s proposal is to:
- Repeal the individual mandate. Insurers are encouraged to design policies of high quality tailored to individual need. By lowering the cost of insurance for younger and healthier individuals, the Plan will expand coverage without a mandate.
- Repeal the employer mandate, thereby offering employers a wider range of options for subsidizing employees insurance.
- Keep the exchanges to provide broad access as well as subsidies for those with low incomes.
- Migrate the Medicaid population onto the exchanges.
- Raise the Medicare eligibility age by 4 months per year indefinitely. Over time this will maintain future retirees on exchange-based or employer sponsored health plans.
By gradually moving the Medicaid and Medicare recipients onto the exchanges, both of these very large populations will receive equal quality coverage to everyone else, delivered in a cost effective manner. Mr. Roy estimates that the Plan will expand coverage by 12 million above Obamacare levels by 2025 and reduce the deficit by $8 trillion over 30 years.
This is the sort of major healthcare reform which we need to get entitlement spending under control!